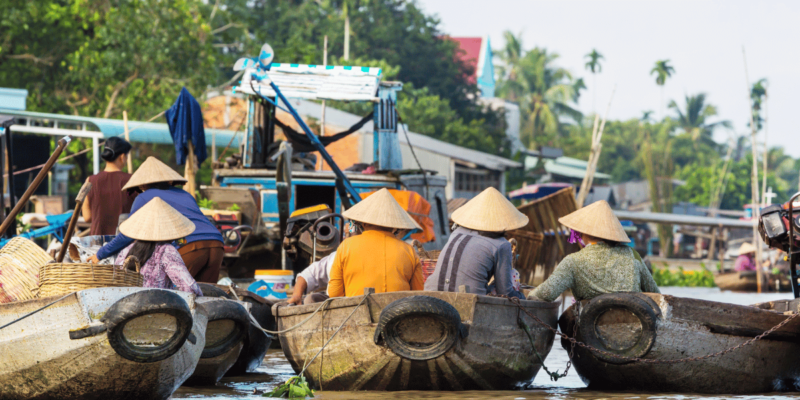
Vietnam’s Historical Narrative
A Tapestry of Struggles and Triumphs
Vietnam’s history is rich and multifaceted, marked by a relentless quest for sovereignty, periods of foreign domination, and profound cultural transformations. Unlike the straightforward historical records that often get bogged down in a web of dates and names, our approach aims to delve into the thematic forces that have sculpted the Vietnamese psyche and societal norms across centuries.
Themes of Resilience and Identity
The enduring spirit of independence is perhaps the most striking theme in Vietnamese history. From the early settlements in the Red River Delta to the modern era, the quest for autonomy has defined the national character. This narrative is punctuated by episodes of foreign rule—most notably a millennium of Chinese control—that introduced new cultural and political dynamics but also ignited fierce resistance.
Confucian Influence and Social Cohesion
The adoption and adaptation of Confucianism provided a framework for social order and governance. More than just a philosophy, it became a way of life that emphasized familial loyalty, social harmony, and respect for hierarchy, deeply influencing Vietnamese social structures and personal relationships.
Cycles of Conquest and Cultural Absorption
Throughout its history, Vietnam has been a crucible for cultural amalgamation. Whether through the forced assimilation during Chinese rule or the voluntary integration of Buddhist teachings, Vietnam demonstrates a unique capacity to absorb external influences and weave them into the fabric of its own culture. This resilience and adaptability are crucial to understanding how Vietnam has maintained its cultural identity despite repeated foreign invasions.
Colonial Legacies and the Path to Modernity
The French colonial period introduced profound changes, bringing Western administrative systems, architecture, and education. However, it also rekindled the Vietnamese drive for independence, culminating in decades of conflict that would eventually shape its contemporary national identity. The struggle against French rule, followed by the conflict with American forces, galvanized a national movement that transcended individual differences in pursuit of a common goal: liberation.
Reunification and Global Integration
Post-war Vietnam faced the monumental task of unifying the country under a single government while rebuilding its economy and international standing. The introduction of Đổi Mới in 1986 marked a pivotal shift from centralized economic planning to a market-oriented approach, sparking economic growth and further integrating Vietnam into the global economy.
Contemporary Challenges and Future Directions
Today, Vietnam stands at a crossroads, balancing traditional values with the pressures of globalization. As it navigates complex international waters, particularly with its pending entry into the World Trade Organization, Vietnam continues to write new chapters in its storied history. These chapters will undoubtedly reflect its enduring themes of resilience and adaptability, as the country strives to preserve its cultural heritage while embracing the opportunities of the 21st century.
A Living History
Understanding Vietnam’s history through these themes offers a richer, more nuanced view of how past events shape current realities and future prospects. It provides a scaffold for visitors to contextualize their experiences and observations while traveling through a country that is both ancient and dynamically modern.