Capital City of Vietnam: Hanoi
Hanoi, the capital city of Vietnam, is a place where history, culture, and modernity converge. As the political and cultural heart of the nation, Hanoi has played a pivotal role in shaping Vietnam’s identity through the ages. From its ancient origins to its current status as a bustling metropolis, Hanoi is a city of contrasts and continuity. This article explores the historical background, cultural significance, political and economic roles, architectural landscape, educational importance, and modern development of Hanoi, providing a comprehensive overview of why this city is central to Vietnam’s past, present, and future.
Historical Background
Hanoi’s history dates back over a thousand years, beginning as a small settlement known as Thang Long (Ascending Dragon) in 1010 when it was established as the capital by Emperor Ly Thai To. The city has witnessed numerous key historical periods, including the Nguyen Dynasty and the influence of French colonialism in the 19th and early 20th centuries. The French left a lasting architectural legacy, evident in the tree-lined boulevards and colonial buildings. After Vietnam’s independence in 1945, Hanoi became the capital of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam, later reunifying the country post-1975. Major historical events, such as the Vietnam War and subsequent economic reforms (Doi Moi), have shaped Hanoi into the vibrant and resilient city it is today.
Cultural Significance
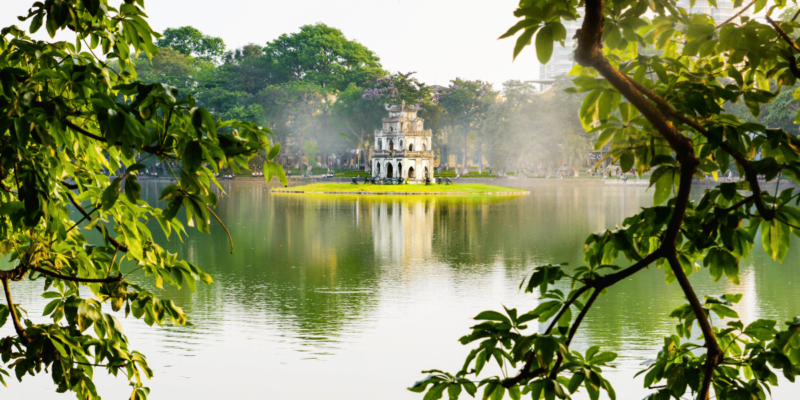
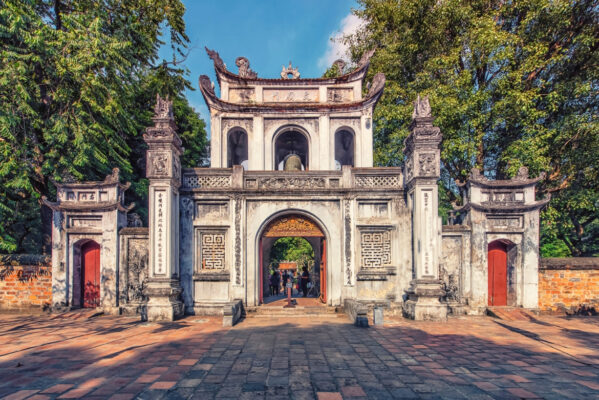
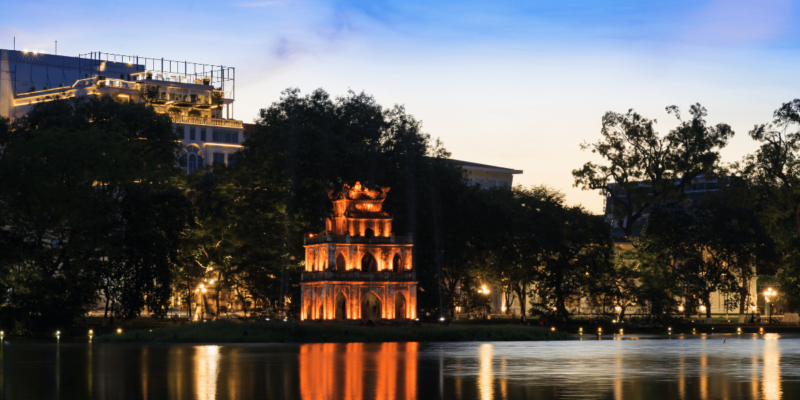
Hanoi is rich in cultural heritage, offering a tapestry of traditional and contemporary Vietnamese culture. Iconic cultural sites such as Hoan Kiem Lake, located in the heart of the city, and the Old Quarter, with its narrow streets and ancient architecture, reflect Hanoi’s historical depth. The Temple of Literature, Vietnam’s first university, founded in 1070, is a symbol of the city’s dedication to education and scholarly pursuits. Hanoi is also known for its vibrant festivals, including Tet (Lunar New Year) and the Mid-Autumn Festival, which are celebrated with much fervour and traditional performances. The city’s commitment to preserving its cultural traditions while embracing modernity makes it a unique cultural hub.
Political and Economic Role
As the capital, Hanoi is the political epicentre of Vietnam, housing key government institutions, including the Presidential Palace, the National Assembly, and numerous ministries. It is also home to various foreign embassies, making it a focal point for international diplomacy. Economically, Hanoi is a significant contributor to Vietnam’s growth, with major industries such as manufacturing, real estate, and tourism driving its economy. Business districts like Ba Dinh and Hoan Kiem are bustling with commercial activity, supported by modern infrastructure. Hanoi’s strategic location and economic policies have played a crucial role in national and regional development, making it a powerhouse in both governance and commerce.
Architectural Landscape
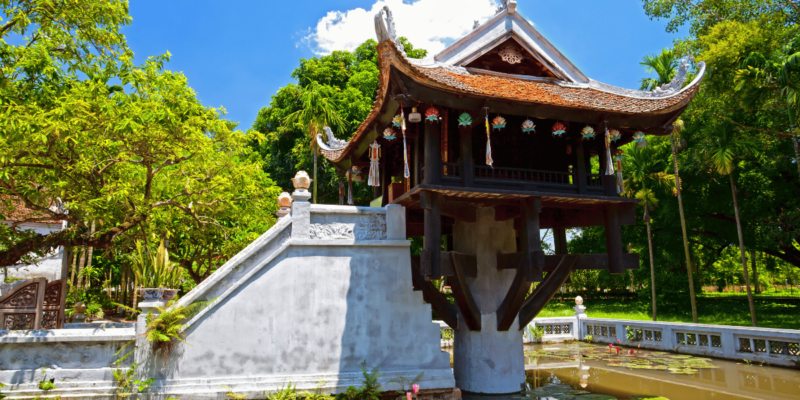
Hanoi’s architectural landscape is a blend of ancient, colonial, and modern influences. The city’s ancient architecture is embodied in historical structures like the One Pillar Pagoda and the Imperial Citadel of Thang Long, both of which offer glimpses into Vietnam’s dynastic past. The French colonial era introduced architectural marvels such as the Hanoi Opera House and St. Joseph’s Cathedral, which add a European charm to the cityscape. In recent years, modern skyscrapers and contemporary buildings have risen, reflecting Hanoi’s rapid urbanisation. The preservation of historical architecture amidst new developments demonstrates Hanoi’s commitment to maintaining its heritage while progressing into the future.
Educational and Intellectual Hub
Hanoi is Vietnam’s leading educational and intellectual hub, home to prestigious universities such as Vietnam National University and Hanoi University of Science and Technology. These institutions are renowned for their academic excellence and research contributions. The city fosters a vibrant intellectual environment, with numerous conferences, seminars, and cultural exchanges taking place regularly. Hanoi’s contributions to science, literature, and the arts are significant, with many Vietnamese scholars, writers, and artists originating from or residing in the city. This educational landscape not only nurtures talent but also drives innovation and cultural development in Vietnam.
Modern Hanoi
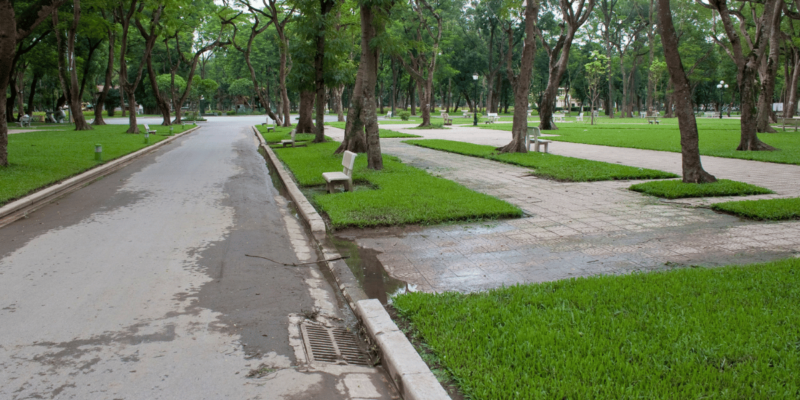
Modern Hanoi is a dynamic metropolis that balances tradition with contemporary living. The city has seen substantial improvements in transportation and infrastructure, including the development of a modern metro system and expanded road networks. Shopping centres, high-rise buildings, and international restaurants reflect the city’s cosmopolitan nature. Emerging trends such as tech startups and green initiatives are shaping Hanoi’s future, attracting young professionals and entrepreneurs. Despite rapid urbanisation, Hanoi maintains its charm with its lakes, parks, and cultural festivals, ensuring a high quality of life for its residents and an enriching experience for visitors.
Conclusion
Hanoi, with its rich historical legacy and vibrant cultural scene, stands as a testament to Vietnam’s enduring spirit and progress. The city’s blend of ancient traditions and modern advancements highlights its unique position as a bridge between the past and the future. As the political, economic, and educational heart of Vietnam, Hanoi continues to play a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s identity and aspirations. Understanding Hanoi’s significance helps us appreciate its contributions to Vietnam’s heritage and its vision for the future, making it not just a capital city but a symbol of the nation’s resilience and dynamism.